Nigeria, like most growing international locations has continued to witness the unfavorable social, financial and political impacts of local weather change. It’s troublesome to determine a hyperlink between local weather change and violent conflicts. Nonetheless, the persistent farmer-herder battle in Nigeria is commonly seen as penalties of shortages of assets like land and waters attributable to local weather change (Alaanuloluwa Ikhuoso et al., 2020). Additional, local weather change is adversely affecting meals safety in Nigeria, and with about 70 % of Nigerian households engaged in agricultural actions, one thing pressing should be carried out to mitigate the approaching disaster. Any makes an attempt to mitigate additional local weather change disaster will rely on collective contribution and collaboration of all international locations of the world together with Nigeria. In 2015, Nigeria was the second highest emitter of greenhouse gases after South Africa, and the manufacturing of oil and fuel within the nation has been linked to steep environmental disasters and social inequalities (Elfredah, 2020). Because of this each developed and growing international locations should successfully contribute to the combat towards local weather change.
Nonetheless, Nigeria being the eight largest suppliers of oil on the planet has a principally monoculture economic system with about 80% of presidency earnings coming from oil income. Because of this makes an attempt by Nigerian state to contribute to the combat towards local weather change would possibly negatively impacts authorities income which in flip impacts state`s capability to handle current local weather change challenges. In different phrases, on the one hand, Nigerian economic system is deeply tied to grease income. Then again, the Nigerian state has continued to undergo from local weather change inflicting socio-economic and political crises. Nonetheless, it isn’t unusual for environmental safety and financial development to be seen as competing goals. Certainly, briefly phrases, insurance policies that defend the atmosphere and people geared toward attaining financial development are sometimes portrayed as conflicting (Checklist & Kunce, 2000). On the fundamental stage, because of this if Nigerian governments had been to handle the environmental disaster and its attendant socio-economic and political crises, it must scale back its dependency on oil income which might have an effect on state`s capability to realize financial development and create jobs.
What do Nigerians take into consideration this climate-economic conundrum? What explains the alternatives between economic system and the atmosphere? For a few years, research on local weather change in Nigeria have targeted on the unfavorable impacts of worldwide warming on the Nigerian society with particular emphasis on its social, financial and political penalties (Edeh et al., 2014; Emodi & Ekene, 2016; Ezegwu, 2014; Sayne, 2011). Different research have seemed on the direct linkage between local weather change and violent conflicts in Nigeria (Adejobi & Fatile, 2012; Alaanuloluwa Ikhuoso et al., 2020; Worldwide Disaster Group, 2020). Nonetheless, few research have explored the contradictions between unfavorable impacts of local weather change in Nigeria and Nigeria`s oil economic system with its environmental degradation capacities. And extra importantly, few research discover what Nigerians take into consideration the dilemma of selecting between environmental safety and financial development. On this research, I study climate-economic issues in Nigeria. The first goal is to research the components that affect selections between environmental safety and financial development. To investigate the components influencing selections between financial development and safety of the atmosphere in Nigeria, I depend on binary variable of environment-economic consideration out there within the seventh wave of the World Values Survey (WVS) performed in 49 international locations together with Nigeria between 2017-2021. The outcomes of the evaluation present that earnings has a optimistic relationship with alternative of financial development. That’s, the upper the extent of earnings of a person, the rise within the probability of supporting financial development towards environmental safety. Secondly, although people with proper wing political orientation will seemingly assist financial development towards atmosphere safety, this relationship was not statistically important. In different phrases, there is no such thing as a statistically important relationship between left-right political place and environment-economic consideration.
Idea
Local weather change is among the defining challenges of the twenty first century that has generated intense debates and controversies amongst governments, teachers and coverage makers. Scholarly discussions on local weather change and financial development have usually targeted on the unfavorable impacts of local weather change on financial development and improvement. There are growing theoretical and empirical proof on the extent and nature of the damages of local weather change on the economic system. Local weather change as we all know it causes the destruction of the ecosystems by way of flood, drought, in addition to deaths of animals resulting in everlasting damages to the society. Moreover, the assets utilized in managing the challenges of worldwide warming might have in any other case been invested in financial, infrastructures, and analysis and improvement (Ali, 2012; Pindyck, 2011). Research by (Dell et al., 2012), utilizing a panel of 136 international locations from 1950-2003 discovered local weather change (1°C) to have lowered financial development in growing nation by 1.3 proportion factors. In accordance with the research, increased temperatures due local weather change even have wide-ranging results together with lowering agricultural and industrial output and in addition growing political instability (Dell et al., 2012).
For a few years, developed international locations have behaved extra irresponsibly in the direction of the atmosphere (Bowen et al., 2012; Reddy & Assenza, 2009). Nonetheless, analysis has proven unfavorable impacts of local weather change to be extra devastating in growing international locations than developed international locations (Bowen et al., 2012; World Financial institution, 2010). It’s because most economies in growing international locations rely closely on agriculture which is extremely delicate to local weather change. Moreover, growing international locations have much less adaptive capacities to deal with the unfavorable penalties of local weather change evaluate to developed international locations (Bowen et al., 2012).
Present research on local weather change in growing international locations deal with the challenges of local weather change in addition to coverage responses of growing international locations to those challenges. Reddy & Assenza (2009) of their research on growing international locations` views on local weather change, argue that market-based response is one of the best coverage response of growing international locations to local weather (Reddy & Assenza, 2009). By this, they imply that growing international locations ought to deal with their improvement priorities first earlier than any local weather change issues. This argument was additional supported by (Maikasuwa, 2013) who suggests the introduction of holistic and pragmatic responses that meet the realities of the developmental wants of the individuals dwelling in growing international locations. In accordance with Maikasuwa (2013), “it’s extra compelling and fascinating for growing international locations to undertake coverage frameworks that may reply to their home exigencies first earlier than these of the worldwide system. It’s subsequently strongly instructed that environmental insurance policies should be people-friendly, people-centred and people-driven”.
This paper will construct on this literature by inspecting what Nigerian individuals principally take into consideration local weather change and financial issues. Although research focusing straight on this topic are restricted, there are huge physique of data with deal with inhabitants notion of local weather change in relations to their livelihoods. For instance, a research by (Elum et al., 2017) examines farmers` notion of local weather change in South Africa. The research reported unfavorable notion of local weather change by farmers in South Africa although many of those farmers developed varied climate-response methods together with planting of drought-tolerant crops. One other research by (Haque et al., 2012) on notion of Bangladeshis to local weather change reported clear notion of local weather change among the many individuals which included elevated warmth, total hotter winters, lowered rainfall. Extra importantly, the research reported unfavorable notion of local weather change by way of its results on technique of dwelling, human well being, agriculture and total livelihoods. This discovering was additionally confirmed by one other research by (Kais & Islam, 2019) which focuses on shrimp-farmers in coastal areas of Bangladesh. The research reported that native shrimp-farmers related local weather change to extend frequency of extremes occasions like cyclones and storm surges in addition to with temperature enhance which threatened their conventional sources of livelihood and their high quality of life.
With completely different targets, a research by Chou (2013) focuses on residents` angle in the direction of the alternatives between financial development and environmental safety. It additionally explores residents` notion of local weather change threat and the power of the federal government to handle the chance. Regarding the dilemma between environmental safety and financial development, about 69% of the individuals within the research didn’t suppose environmental safety can hinder financial development (Chou, 2013). In different phrases, they consider that each environmental safety and financial development can co-exist collectively. An analogous research by Begum and Pereira (2015) amongst company managers in Malaysia mirror a a lot optimistic notion of environmental safety in relations to financial development. Although the individuals famous the seemingly unfavorable affect of local weather change on their firms` income, greater than 95% of them believed that local weather change would don’t have any impact on the economic system of Malaysia (Begum & Pereira, 2015).
Additional research have additionally deal with the angle in the direction of local weather change in occasions of extreme financial challenges. That’s, what do individuals take into consideration local weather change when there may be financial meltdown. For instance, a research by Papoulis and co-authors (2015), study the angle of residents of Greece in the direction of local weather change throughout extreme financial disaster. In accordance with their findings, although residents of Greece had been conscious of local weather change, they didn’t believe within the capability and capability of the federal government to handle local weather change in a method that can even defend the economic system.
These research above principally doc residents` notion of impacts of local weather change they usually lacked predictive capabilities of things influencing unfavorable or optimistic notion of local weather change in these international locations. Most of the research additionally failed to think about the dichotomy between environmental safety and financial development. Nonetheless, out there research with goal nearer or just like this principally targeted on western developed societies (Egan & Mullin, 2012; Hamilton, 2011; McCright & Dunlap, 2011). Their analyses present that right-wing political orientation are principally beneficial in the direction of financial consideration as towards environmental safety. For instance, a research by (Ziegler, 2017) examines the components that affect local weather change beliefs and altitudes in Germany, The US and China. Although the research reported important affect of political orientation on local weather change beliefs and altitudes, it was much less impactful than environmental values measured utilizing New Ecological Paradigm (NEP) scale in predicting attitudes and beliefs to local weather change. Nonetheless, US and German residents with right-wing political orientation expressed considerably much less assist for publicly financed local weather coverage.
With barely completely different goal, a complete cross nationwide research by (Knight, 2016) study notion of local weather change dangers throughout completely different international locations whereas specializing in components that affect unfavorable or optimistic attitudes towards local weather change. In accordance with the findings of the research, residents of wealthier and extremely educated international locations are typically extra conscious of local weather change. Nonetheless, the research discovered no conclusive proof on the affect of political orientation and vulnerability to local weather change on unfavorable or optimistic attitudes towards local weather change. The research additionally reported inconsistent outcomes concerning the affect of unemployment and stage of schooling on local weather change threat consciousness.
Although these research targeted totally on western societies, they supply fundamental clarification of things that affect local weather change consciousness and optimistic or unfavorable attitudes in the direction of local weather change. Alongside the identical line, although specializing in a growing nation, Nigeria, this present research makes an attempt to doc the affect of political orientation on the alternatives between environmental safety and financial development. Primarily based on findings of current literature, I anticipate that right-wing political orientation will favour financial development towards environmental safety. I subsequently hypothesize that:
H1: right-wing political orientation favours financial development towards environmental safety.
Additional research have mentioned the function of earnings or inequalities on residents notion of affect of local weather change. On the one hand, proof has proven that poor members of the society are prone to be extra negatively impacted by local weather change whereas additionally lowering their capability to deal with unfavorable impacts of local weather change (Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change, 2014; Islam & Winkel, 2017; Skoufias & Financial institution, 2012). Then again, wealthy member of the society or residents of wealthier international locations are inclined to downplay the chance of local weather change in comparison with the residents of poor international locations or poor members of the society (Lo & Chow, 2015; McCright & Dunlap, 2011). It’s because ample financial assets probably present sense of safety and safety towards environmental crises. Given this actuality, I anticipate that people with excessive earnings in middle-income international locations like Nigeria will favour financial development towards environmental safety. I hypothesize that:
H2: excessive earnings earners or excessive stage of earnings will favor financial development towards environmental safety.
Methodology
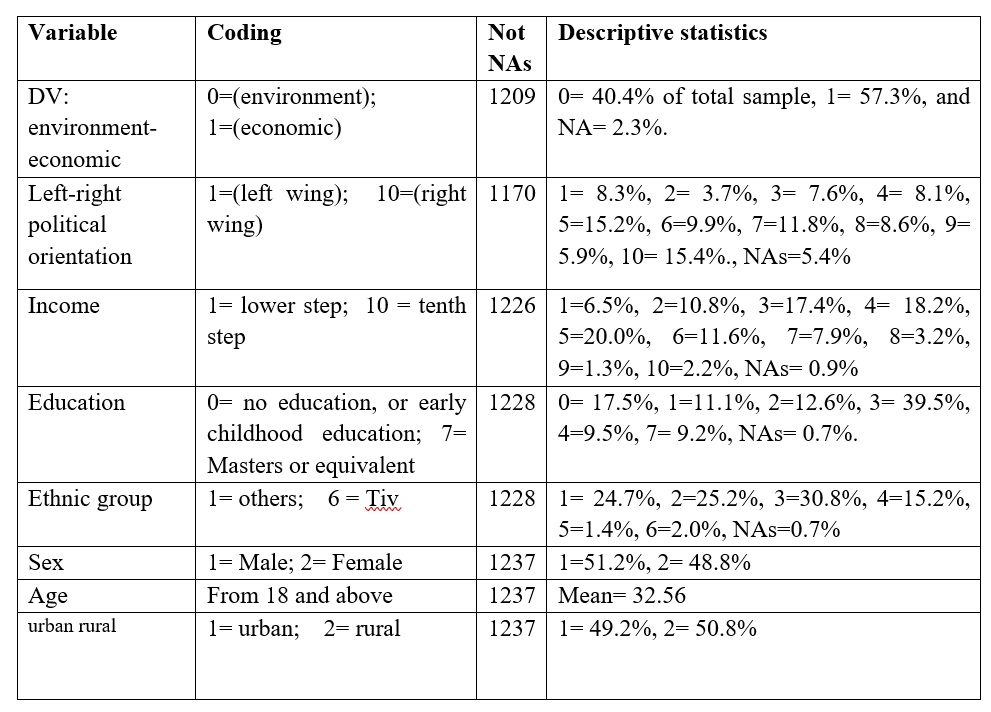
This research makes use of a survey information sourced from seventh wave of the World Values Survey (WVS) performed in 49 international locations together with Nigeria between 2017-2021. About 50 international locations world wide participated within the seventh wave of the survey with greater than 70, 000 respondents and it’s newest information out there as of April 4, 2021. Basically, the World Values Survey asks residents of collaborating international locations their opinions on points regarding politics, democracy, governance, worldwide politics in addition to completely different socio-demographic questions. The survey information for Nigeria was collected in 2018 and it accommodates 1, 237 individuals chosen by way of random chance consultant samples. Within the nation documentation specializing in Nigeria, there have been attention-grabbing questions particularly specializing in local weather change and financial development. One among them, used for this evaluation requested respondents in the event that they (a) suppose defending the atmosphere needs to be given precedence even when it causes slower financial development and a few lack of jobs or (b) financial development and creating jobs needs to be the highest precedence, even when the atmosphere suffers to some extent. This makes a binary variable of atmosphere protection-economic development.
My goal is to know the predictors of the alternatives between environmental safety or financial development are, subsequently, I used this binary variable of atmosphere protection-economic development as my dependent variable in two logistic regression analyses. My first mannequin examines the affect of left-right placement on atmosphere protection-economic development. The left-right placement variable varies from 1 to 10 with 1 corresponding to finish left placement and 10 corresponding to finish proper placement. My second mannequin retains the binary dependent variable of environmental safety or financial development and I explored the affect of stage of earnings on the alternatives between financial development and environmental safety. The extent of earnings variable varies from 1 (lowest earnings group) to 10 (highest earnings group).
Within the two logit regression fashions, I managed for the next variables: age, schooling attainment stage, faith, ethnic group and gender, intercourse, place of residence (city or rural) . The age variable ranges from 18 years to 70 years with a imply age of 32 years. The schooling attainment stage variable strikes from no schooling to Grasp or equal schooling. The Faith variable consists of main non secular teams in Nigeria: Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim and different varieties of Christian denominations. Gender variable was a binary variable of female and male.
Dialogue of Outcomes and Evaluation
Environmental Safety and Financial Progress
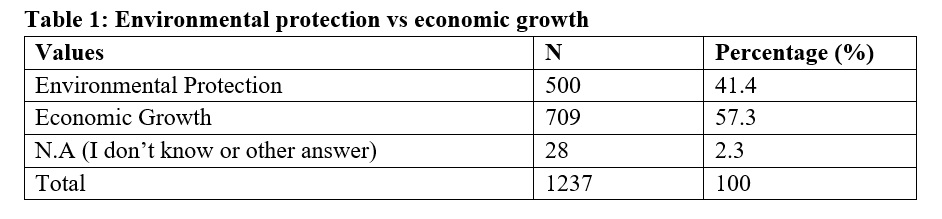
The primary necessary discovering from our evaluation is the respondents assist for environmental safety or financial development. As introduced Desk 1 (See Appendix), about 41% of the overall respondents reported assist for environmental safety even when it causes slower financial development and lack of jobs. Greater than have of the respondents (57%) reported assist for financial development even when the atmosphere suffers because of it. Solely about 2% of the respondent didn’t reply the query or don’t know the reply. This demonstrates that on common, for a lot of Nigerians, there’s a barely extra assist for financial development towards environmental safety.
Surroundings-Financial and Left-Proper Political Orientation
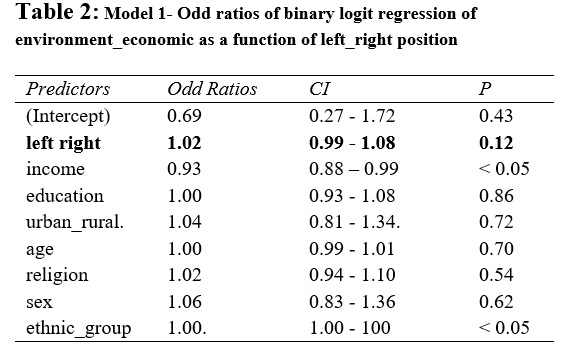
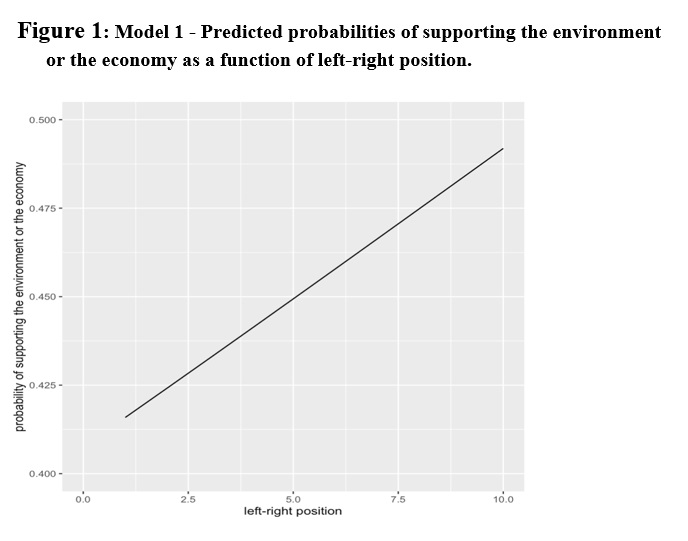
The outcomes of the primary logistic regression evaluation in Desk 2 and Determine 1 (See Appendix) reveal that the connection between environmental safety versus financial development and left-right place is just not statistically important although there’s a optimistic relationship. As left-right place strikes from left to proper wing place, the probability of supporting the economic system towards the atmosphere additionally will increase. The determine 1 exhibiting the anticipated chances of environment-economic as a perform of left-right place (See Appendix) reveals that a person with proper wing political orientation has about 48% (0.485) chance of supporting financial development towards environmental safety. Whereas a person with the left wing political orientation has a bit of over 41% (0.41) chance of supporting financial development towards environmental safety. Additional, as particular person strikes from left wing to proper wing, the chance of supporting the economic system towards environmental safety additionally will increase (Determine 1). Nonetheless, as seen in Desk 2 (See Appendix), the connection between environment-economic and left-right place is just not statistically important (P.V = 0.12), subsequently, we settle for the null speculation and reject the speculation that “right-wing political orientation favours financial development towards environmental safety”
These outcomes didn’t affirm the speculation that proper wing political orientation favours financial development towards environmental safety, therefore the rejection of the speculation. Nonetheless, the outcomes present that these with proper wing political orientation are prone to assist financial development (not statistically important). Due to this fact, the outcomes present perception on what the connection between political orientation and environment-economic consideration may very well be. Utilizing completely different information set, it might be attention-grabbing if different analysis can additional discover the connection between political orientation and assist for the economic system towards environmental safety in Nigeria.
Surroundings-Financial and Revenue
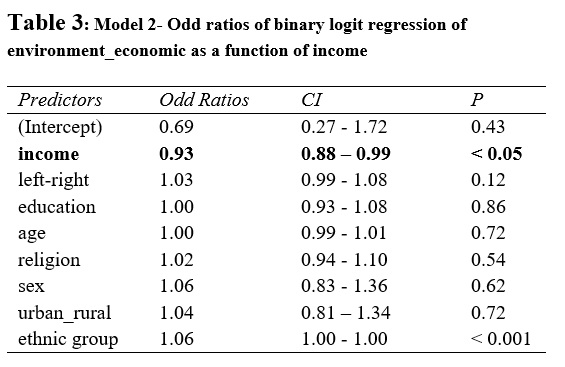
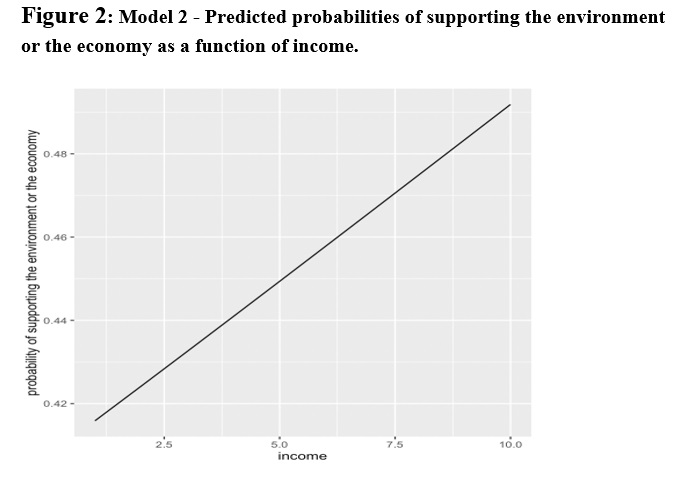
The outcomes of the second logistic regression mannequin present the impact of earnings on environmental safety vs financial development. The mannequin studies a statistically important relationship between environmental safety vs financial development and earnings (see Desk 3 & Determine 2 in Appendix). As earnings will increase, the probability of assist for the economic system towards the atmosphere additionally will increase. As the anticipated chances (see Determine 2 in Appendix) reveals, a person within the highest earnings stage has about 49% (0.491) chance of supporting financial development towards environmental safety. Whereas a person within the lowest earnings stage has a bit of beneath 42% (0.41) chance of supporting financial development towards environmental safety. This confirms the speculation that prime earnings earners will favor financial development towards environmental safety. Nigerians throughout the highest earnings bracket usually tend to assist financial development forward of environmental safety and as their earnings will increase, the chance of supporting the economic system additionally will increase.
These findings increase on current literature on the impact of earnings on environmental threat notion. As reported by Low & Chow (2015), wealthy members of the society in wealthier international locations are inclined to downplay environmental dangers. Nonetheless, our findings present that wealthy individuals in poor or growing international locations are additionally prone to downplay environmental threat or a minimum of consider it isn’t as necessary as financial development. These findings have necessary implications for environmental safety insurance policies in societies like Nigeria. It implies that any given environmental safety insurance policies that negatively affect on financial development or that’s perceived to be negatively impacting on the economic system perhaps rejected by wealthier members of the society.
Diagnostic of Fashions
I performed a McFadden mannequin match evaluation. Nonetheless, the outcomes present that each fashions don’t present a very good match to research the variance of the dependent variable. Each fashions have a McFadden’s pseudo-r2 of 0.016 and 0.016, that means that they every clarify solely about 1.6% of the variance of the dependent variable, environment-economy. Certainly, this can be a very low measure, and it means the mannequin didn’t do nicely. I can not at the moment clarify why the mannequin has carried out badly particularly given the actual fact I’ve included all impartial variables that intuitively make sense within the logistic regression.
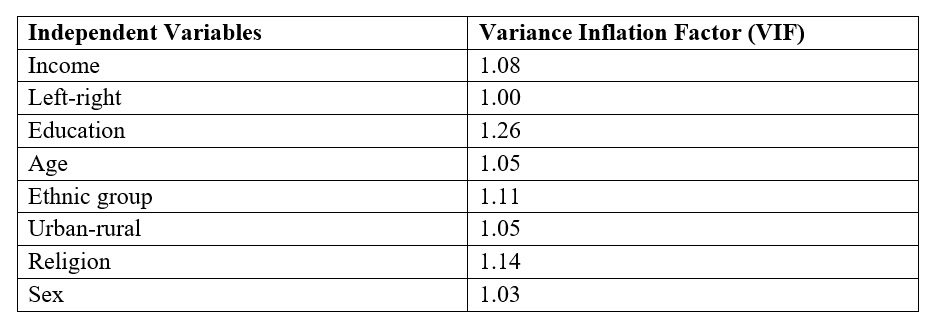
Nonetheless, the mannequin don’t undergo from multicollinearity. A take a look at of Variance Inflation Issue (VIF) reveals that not one of the impartial variables is above 1.2 (see Appendix). The smallest attainable worth of VIF is one (absence of multicollinearity). As a rule of thumb, a VIF worth that exceeds 5 or 10 signifies a problematic quantity of collinearity (James et al., 2013). Since not one of the impartial variables has VIF that’s above 1.2, the fashions don’t undergo from multicollinearity.
Conclusion
This research examines the attitude of Nigerians on local weather change and financial development issues. Present research have targeted on components that affect notion of local weather change dangers particularly in developed international locations. With a barely completely different goal, I examined the components that affect selections between environmental safety and financial development. The findings present that left-right political orientation doesn’t have statistically important relationship on environment-economic issues, although proper wing political orientation will increase the probability of supporting financial development towards environmental safety thereby supporting current literature. Because of this there is no such thing as a statistically important proof that left-right political orientation influences environment-economic consideration. Nonetheless, additional analysis can discover this relationship with one other dataset.
The outcomes of the second logistic mannequin present that there’s a statistically important relationship between environment-economic and earnings. As earnings will increase, the probability of supporting financial development towards environmental safety additionally will increase. This discovering has critical implication for environmental safety insurance policies. On the fundamental stage, environmental insurance policies of presidency that threatens financial development might not be supported by wealthy members of the society resulting from the truth that they’re downplaying environmental dangers. Or as a result of they suppose the economic system is simply extra necessary than the atmosphere. Due to this fact, authorities should design environmental safety insurance policies extra rigorously or in a method that doesn’t threaten financial development.
Appendix
A). Outcomes
B). Variables of curiosity
Q111, Q240, Q288, Q275, Q262, Q289, Q290, Q260, H_URBRURAL.
Dependent variable survey query:
Listed here are two statements individuals generally make when discussing the atmosphere. Which ones comes nearer to your personal viewpoint? A). Defending the atmosphere needs to be given precedence, even when it causes slower financial development and a few lack of jobs. B). Financial development and creating jobs needs to be the highest precedence, even when the atmosphere suffers to some extent.
Coding:
1 (defending atmosphere), 2 (economic system development and creating jobs). I recorded them to 0 (defending atmosphere), and 1(financial development).
C). Multicollinearity Take a look at (Variance Inflation Issue)
D). Abstract of the variables used within the regression fashions
Bibliography
Adejobi, O., & Fatile, O. (2012). Local weather Change, Surroundings and Conflicts in Nigeria. British Journal of Arts and Social Sciences ISSN: 2046-9578.
Alaanuloluwa Ikhuoso, O., Adegbeye, M. J., Elghandour, M. M. Y., Mellado, M., Al-Dobaib, S. N., & Salem, A. Z. M. (2020). Local weather change and agriculture: The competitors for restricted assets amidst crop farmers-livestock herding battle in Nigeria – A evaluate. Journal of Cleaner Manufacturing, 272, 123104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123104
Ali, S. N. (2012, February 1). Local weather Change and Financial Progress in a Rain-fed Economic system: How A lot Does Rainfall Variability Price Ethiopia? Africa Portal; Ethiopian Economics Affiliation (EEA). https://www.africaportal.org/publications/climate-change-and-economic-growth-in-a-rain-fed-economy-how-much-does-rainfall-variability-cost-ethiopia/
Begum, R. A., & Pereira, J. J. (2015). The attention, notion and motivational evaluation of local weather change and enterprise views in Malaysia. Mitigation and Adaptation Methods for International Change, 20(3), 361–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-013-9495-6
Bowen, A., Cochrane, S., & Fankhauser, S. (2012). Local weather change, adaptation and financial development. Climatic Change, 113(2), 95–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0346-8
Chou, Okay. T. (2013). The general public notion of local weather change in Taiwan and its paradigm shift. Vitality Coverage, 61, 1252–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.06.016
Dell, M., Jones, B. F., & Olken, B. A. (2012). Temperature Shocks and Financial Progress: Proof from the Final Half Century. American Financial Journal: Macroeconomics, 4(3), 66–95. https://doi.org/10.1257/mac.4.3.66
Edeh, H. C., Leo-Nnoli, T. C., & Eme, I. O. (2014). The Political Economic system of Local weather Change in Africa: Nigeria in Perspective. Nigerian Chapter of Arabian Journal of Enterprise and Administration Overview, 2(7), 18–29. https://doi.org/10.12816/0011607
Egan, P. J., & Mullin, M. (2012). Turning Private Expertise into Political Attitudes: The Impact of Native Climate on People’ Perceptions about International Warming. The Journal of Politics, 74(3), 796–809. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022381612000448
Elfredah, Okay.-A. (2020). ‘Our Neighborhood Has Been Struggling’: Complete Abandons Nigerian Hospital Constructed as Compensation for Fuel Pipeline Explosion. DeSmog UK. https://www.desmog.co.uk/2020/03/20/total-abandon-nigeria-hospital
Elum, Z. A., Modise, D. M., & Marr, A. (2017). Farmer’s notion of local weather change and responsive methods in three chosen provinces of South Africa. Local weather Danger Administration, 16, 246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2016.11.001
Emodi, N., & Ekene, N. (2016). Local weather Change and Its Impression in Nigerian Economic system. Journal of Scientific Analysis & Studies, 10, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.9734/JSRR/2016/25162
Ezegwu, C. (2014). Local weather Change in Nigeria: The Impacts and Adaptation Methods (SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 2543940). Social Science Analysis Community. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2543940
Hamilton, L. C. (2011). Schooling, politics and opinions about local weather change proof for interplay results. Climatic Change, 104(2), 231–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9957-8
Haque, M. A., Yamamoto, S. S., Malik, A. A., & Sauerborn, R. (2012). Households’ notion of local weather change and human well being dangers: A neighborhood perspective. Environmental Well being, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-11-1
Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change. (2014). Local weather Change 2014 – Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Half B: Regional Features: Working Group II Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Evaluation Report: Quantity 2: Regional Features (Vol. 2). Cambridge College Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415386
Worldwide Disaster Group. (2020, September 28). Local weather Change Doesn’t Must Stoke Battle. Disaster Group. https://www.crisisgroup.org/international/climate-change-doesnt-have-stoke-conflict
Islam, S. N., & Winkel, J. (2017). Local weather Change and Social Inequality. 32.
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2013). An Introduction to Statistical Studying: With Functions in R. Springer-Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7138-7
Kais, S. M., & Islam, M. S. (2019). Notion of Local weather Change in Shrimp-Farming Communities in Bangladesh: A Essential Evaluation. Worldwide Journal of Environmental Analysis and Public Well being, 16(4), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040672
Knight, Okay. W. (2016). Public consciousness and notion of local weather change: A quantitative cross-national research. Environmental Sociology, 2(1), 101–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/23251042.2015.1128055
Checklist, J. A., & Kunce, M. (2000). Environmental Safety and Financial Progress: What Do the Residuals Inform Us? Land Economics, 76(2), 267–282. https://doi.org/10.2307/3147228
Lo, A. Y., & Chow, A. T. (2015). The connection between local weather change concern and nationwide wealth. Climatic Change, 131(2), 335–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1378-2
Maikasuwa, S. A. (2013). CLIMATE CHANGE AND DEVELOPING COUNTRIES: ISSUES AND POLICY IMPLICATION. 1, 10.
McCright, A. M., & Dunlap, R. E. (2011). Cool dudes: The denial of local weather change amongst conservative white males in the USA. International Environmental Change, 21(4), 1163–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.06.003
Papoulis, D., Kaika, D., Bampatsou, C., & Zervas, E. (2015). Public Notion of Local weather Change in a Interval of Financial Disaster. Local weather, 3(3), 715–726. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli3030715
Pindyck, R. (2011). Fats Tails, Skinny Tails, and Local weather Change Coverage. Overview of Environmental Economics and Coverage, 5(2), 258–274. https://econpapers.repec.org/article/ouprenvpo/v_3a5_3ay_3a2011_3ai_3a2_3ap_3a258-274.htm
Reddy, B. S., & Assenza, G. B. (2009). Local weather change—A growing nation perspective. 14.
Sayne, A. (2011). Local weather Change Adaptation and Battle in Nigeria. 16.
Skoufias, E., & Financial institution, the W. (2012). The poverty and welfare impacts of local weather change quantifying the results, figuring out the difference methods. World Financial institution. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/deal with/10986/9384/714510PUB097800C0disclosed070250120.pdf?sequence=1
World Financial institution. (2010). World improvement report 2010: Growth and local weather change [Text/HTML]. World Financial institution. https://paperwork.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/201001468159913657/World-development-report-2010-development-and-climate-change
Ziegler, A. (2017). Political orientation, environmental values, and local weather change beliefs and attitudes: An empirical cross-country evaluation. Vitality Economics, 63, 144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.01.022
