Google Prey —
Crooks discover new methods to stop Google from detecting malicious packages.
Dan Goodin –

Researchers mentioned they’ve found a batch of apps downloaded from Google Play greater than 300,000 instances earlier than the apps had been revealed to be banking trojans that surreptitiously siphoned person passwords and two-factor authentication codes, logged keystrokes, and took screenshots.
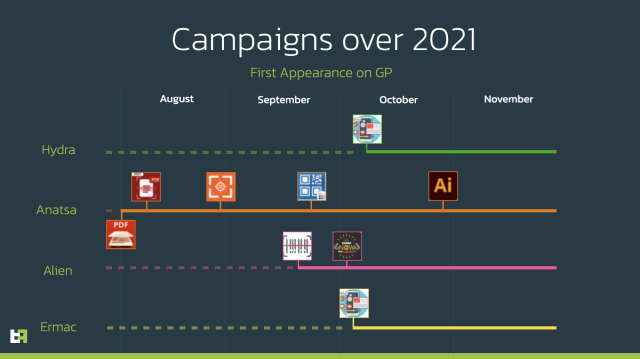
The apps—posing as QR scanners, PDF scanners, and cryptocurrency wallets—belonged to 4 separate Android malware households that had been distributed over 4 months. They used a number of methods to sidestep restrictions that Google has devised in an try to rein within the never-ending distribution of fraudulent apps in its official market. These limitations embrace limiting using accessibility providers for sight-impaired customers to stop the automated set up of apps with out person consent.
Small footprint
“What makes these Google Play distribution campaigns very tough to detect from an automation (sandbox) and machine studying perspective is that dropper apps all have a really small malicious footprint,” researchers from cellular safety firm ThreatFabric wrote in a put up. “This small footprint is a (direct) consequence of the permission restrictions enforced by Google Play.”
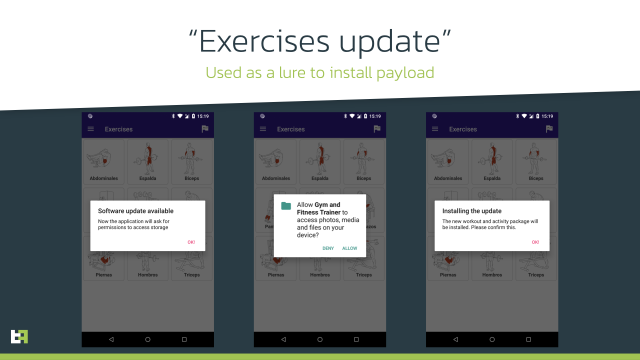
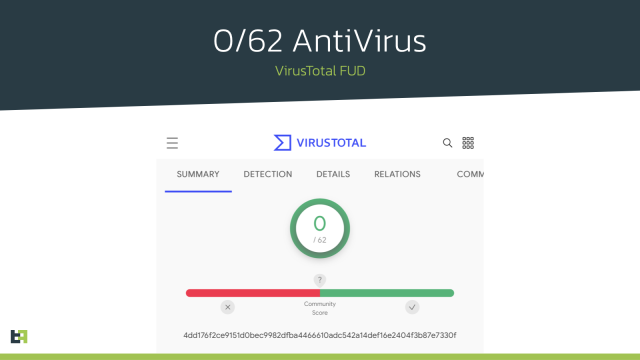
As a substitute, the campaigns usually delivered a benign app at first. After the app was put in, customers acquired messages instructing them to obtain updates that put in extra options. The apps typically required updates to be downloaded from third-party sources, however by then, many customers had come to belief them. A lot of the apps initially had zero detections by malware checkers accessible on VirusTotal.
ThreatFabric
The apps additionally flew beneath the radar by utilizing different mechanisms. In lots of instances, the malware operators manually put in malicious updates solely after checking the geographic location of the contaminated telephone or by updating telephones incrementally.
“This unimaginable consideration devoted to evading undesirable consideration renders automated malware detection much less dependable,” the ThreatFabric put up defined. “This consideration is confirmed by the very low general VirusTotal rating of the 9 variety of droppers we’ve investigated on this blogpost.”
The malware household liable for the most important variety of infections is called Anatsa. This “moderately superior Android banking trojan” provides quite a lot of capabilities, together with distant entry and computerized switch methods, which mechanically empty victims’ accounts and ship the contents to accounts belonging to the malware operators.
The researchers wrote:
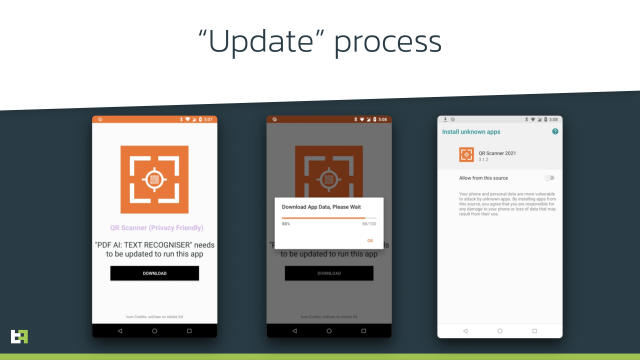
The method of an infection with Anatsa seems to be like this: upon the beginning of set up from Google Play, the person is pressured to replace the app so as to proceed utilizing the app. On this second, [the] Anatsa payload is downloaded from the C2 server(s) and put in on the system of the unsuspecting sufferer.
Actors behind it took care of creating their apps look legit and helpful. There are giant numbers of optimistic critiques for the apps. The variety of installations and presence of critiques could persuade Android customers to put in the app. Furthermore, these apps certainly possess the claimed performance; after set up, they do function usually and additional persuade [the] sufferer [of] their legitimacy.
Regardless of the overwhelming variety of installations, not each system that has these droppers put in will obtain Anatsa, because the actors made efforts to focus on solely areas of their curiosity.
ThreatFabric
Three different malware households discovered by the researchers included Alien, Hydra, and Ermac. One of many droppers used to obtain and set up malicious payloads was generally known as Gymdrop. It used filter guidelines based mostly on the mannequin of the contaminated system to stop the focusing on of researcher gadgets.
New exercise workouts
“If all situations are met, the payload will probably be downloaded and put in,” the put up said. “This dropper additionally doesn’t request Accessibility Service privileges; it simply requests permission to put in packages, spiced with the promise to put in new exercise workouts—to entice the person to grant this permission. When put in, the payload is launched. Our menace intelligence exhibits that in the mean time, this dropper is used to distribute [the] Alien banking trojan.”
The researchers listed 12 Android apps that participated within the fraud. The apps are:
| App title | Bundle title | SHA-256 |
|---|---|---|
| Two Issue Authenticator | com.flowdivison | a3bd136f14cc38d6647020b2632bc35f21fc643c0d3741caaf92f48df0fc6997 |
| Safety Guard | com.protectionguard.app | d3dc4e22611ed20d700b6dd292ffddbc595c42453f18879f2ae4693a4d4d925a |
| QR CreatorScanner | com.prepared.qrscanner.combine | ed537f8686824595cb3ae45f0e659437b3ae96c0a04203482d80a3e51dd915ab |
| Grasp Scanner Stay | com.multifuction.mix.qr | 7aa60296b771bdf6f2b52ad62ffd2176dc66cb38b4e6d2b658496a6754650ad4 |
| QR Scanner 2021 | com.qr.code.generate | 2db34aa26b1ca5b3619a0cf26d166ae9e85a98babf1bc41f784389ccc6f54afb |
| QR Scanner | com.qr.barqr.scangen | d4e9a95719e4b4748dba1338fdc5e4c7622b029bbcd9aac8a1caec30b5508db4 |
| PDF Doc Scanner – Scan to PDF | com.xaviermuches.docscannerpro2 | 2080061fe7f219fa0ed6e4c765a12a5bc2075d18482fa8cf27f7a090deca54c5 |
| PDF Doc Scanner | com.docscanverifier.cellular | 974eb933d687a9dd3539b97821a6a777a8e5b4d65e1f32092d5ae30991d4b544 |
| PDF Doc Scanner Free | com.doscanner.cellular | 16c3123574523a3f1fb24bbe6748e957afff21bef0e05cdb3b3e601a753b8f9d |
| CryptoTracker | cryptolistapp.app.com.cryptotracker | 1aafe8407e52dc4a27ea800577d0eae3d389cb61af54e0d69b89639115d5273c |
| Gymnasium and Health Coach | com.health club.coach.jeux | 30ee6f4ea71958c2b8d3c98a73408979f8179159acccc01b6fd53ccb20579b6b |
| Gymnasium and Health Coach | com.health club.coach.jeux | b3c408eafe73cad0bb989135169a8314aae656357501683678eff9be9bcc618f |
ThreatFabric
Requested for remark, a Google spokesman pointed to this put up from April detailing the corporate’s strategies for detecting malicious apps submitted to Play.
Over the previous decade, malicious apps have plagued Google Play frequently. As was the case this time, Google is fast to take away the fraudulent apps as soon as it has been notified of them, however the firm has been chronically unable to seek out 1000’s of apps which have infiltrated the bazaar and contaminated 1000’s and even hundreds of thousands of customers.
It’s not at all times simple to identify these scams. Studying person feedback may also help, however not at all times, since crooks typically seed their submissions with faux critiques. Steering away from obscure apps with small person bases may also assist, however that tactic would have been ineffective on this case. Customers also needs to consider carefully earlier than downloading apps or app updates from third-party markets.
The very best recommendation for staying protected from malicious Android apps is to be extraordinarily sparing in putting in them. And if you happen to haven’t used an app for some time, uninstalling it’s a good suggestion.

